A Deep Psychological Perspective
In modern life—marked by digital overload, economic uncertainty, social comparison, and emotional burnout—Maslow’s theory feels more relevant than ever. However, the way these needs are met today looks very different from Maslow’s original context.
This article explores each level of Maslow’s hierarchy, how it appears in contemporary life, and why unmet needs often show up as stress, anxiety, relationship issues, and emotional exhaustion.
Understanding Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
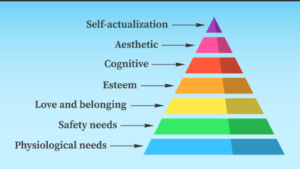
Maslow proposed that human needs are organized in a hierarchical structure, often represented as a pyramid. According to the theory:
-
Lower-level needs must be reasonably satisfied before higher-level needs become dominant
-
Human motivation is driven by unmet needs
-
Psychological health is not just the absence of illness, but the presence of growth
The five classic levels are:
-
Physiological Needs
-
Safety Needs
-
Love and Belonging
-
Esteem
-
Self-Actualization
(Modern psychology also recognizes Self-Transcendence as an extension.)
1. Physiological Needs: Survival in a Fast-Paced World
Core needs
Food, water, sleep, shelter, rest, physical health
Expanded Modern-Life Reality
On the surface, many people appear to meet these needs. However, modern life often satisfies quantity but neglects quality.
People may have:
-
Food, but not nutritional balance
-
Shelter, but not restful sleep
-
Medical access, but not preventive care
-
Beds, but not true rest
Late-night screen use, irregular work hours, financial stress, and constant mental stimulation keep the nervous system in a state of physiological overdrive. The body remains alert when it should be restoring.
Many individuals normalize exhaustion, headaches, gut issues, hormonal imbalance, and chronic pain—treating them as “part of life” rather than warning signals.
Expanded Psychological Impact
When physiological needs are compromised:
-
The brain’s emotional regulation system weakens
-
Stress tolerance drops sharply
-
Small problems feel overwhelming
-
Anxiety intensifies because the nervous system lacks stability
-
Concentration, memory, and decision-making decline
From a therapeutic perspective, psychological insight cannot integrate into a dysregulated body. Talk therapy, motivation techniques, and self-help strategies often fail because the foundation—biological stability—is missing.
💡 Many symptoms labeled as “mental illness” reduce significantly when sleep cycles, nutrition, hydration, and rest are restored consistently.
2. Safety Needs: Emotional and Psychological Security Today
Core needs
Physical safety, financial security, health stability, predictability
Expanded Modern-Life Reality
Unlike earlier eras, danger today is often chronic, invisible, and psychological rather than immediate or physical.
Modern insecurity comes from:
-
Unstable employment and income uncertainty
-
Rising healthcare costs and fear of illness
-
Relationship unpredictability and emotional inconsistency
-
Constant exposure to distressing global news
-
Unresolved childhood trauma resurfacing under adult stress
Even when life appears “stable,” the body may not feel safe. For many adults, early experiences of neglect, abuse, or chaos create a permanent internal alarm system.
Expanded Psychological Impact
When safety needs are unmet, the nervous system remains in survival mode:
-
Generalized anxiety and constant worry emerge
-
Hypervigilance becomes normal
-
Control issues develop as a way to feel safe
-
Trust becomes difficult, even in healthy relationships
-
Emotional numbness replaces vulnerability as self-protection
🔍 Clinically, many high-functioning individuals are unknowingly stuck at the safety level, chasing success or relationships while their nervous system is still focused on survival, not growth.
3. Love and Belonging: Connection in the Age of Isolation
Core needs
Love, affection, intimacy, friendship, belongingness
Expanded Modern-Life Reality
Modern society offers connection without closeness.
People may have:
-
Hundreds of contacts but no emotional safety
-
Online visibility but offline loneliness
-
Relationships based on roles, performance, or utility
-
Fear of vulnerability due to past attachment wounds
Many individuals learned early that love was conditional—earned through obedience, achievement, or emotional suppression. As adults, this translates into people-pleasing, fear of abandonment, or avoidance of intimacy.
Expanded Psychological Impact
When belonging needs are unmet:
-
Loneliness persists even in relationships
-
Depression deepens due to emotional isolation
-
Trauma bonds feel intense and “addictive”
-
Individuals tolerate disrespect to avoid being alone
-
Self-worth becomes externally regulated
❤️ From a healing perspective, humans are biologically wired to heal in safe connection. Emotional safety is not dependency—it is a core developmental need.
4. Esteem Needs: Self-Worth in a Comparison Culture
Core needs
Self-respect, confidence, recognition, competence, autonomy
Maslow distinguished between:
-
Internal esteem: self-worth, mastery, autonomy
-
External esteem: validation, praise, status
Expanded Modern-Life Reality
Today’s culture heavily prioritizes external esteem:
-
Likes, followers, visibility
-
Salary, productivity, titles
-
Achievement over authenticity
Social comparison has become constant and unavoidable. People are exposed to curated success stories without seeing effort, failure, or emotional cost.
Expanded Psychological Impact
When esteem needs are unmet or externally dependent:
-
Imposter syndrome becomes chronic
-
Perfectionism masks deep insecurity
-
Burnout develops from overcompensation
-
Fear of failure prevents exploration
-
Approval becomes addictive
⚠️ When self-worth depends entirely on external validation, emotional stability becomes fragile—rising and falling with feedback.
5. Self-Actualization: Becoming Who You Truly Are
Core needs
Purpose, creativity, authenticity, personal growth, meaning
Self-actualization is not about achievement—it is about alignment between inner values and outer life.
Expanded Modern-Life Reality
Many people appear successful but feel internally disconnected:
-
Careers chosen for security, not meaning
-
Creativity suppressed for approval
-
Identity shaped by expectations
-
A persistent sense of “something is missing”
This level is often blocked not by lack of ability, but by unresolved lower-level needs—especially safety, belonging, and esteem.
Expanded Psychological Impact
Blocked self-actualization often shows up as:
-
Existential anxiety
-
Midlife or identity crises
-
Emotional numbness despite comfort
-
Chronic dissatisfaction without clear cause
🌱 True self-actualization requires:
-
Emotional awareness and honesty
-
Healing unresolved trauma
-
Permission to be authentic
-
Autonomy and self-acceptance
-
Psychological safety to explore identity
Beyond Maslow: Self-Transcendence in Modern Psychology
Later in life, Maslow proposed Self-Transcendence—going beyond the self.
Examples include:
-
Service to others
-
Spiritual growth
-
Contribution to community
-
Legacy and meaning beyond personal gain
In modern therapy, this appears as:
-
Values-based living
-
Compassion-focused work
-
Purpose-driven careers
-
Healing not just for self, but for others
Why Maslow’s Theory Still Matters Today
Maslow’s hierarchy reminds us that:
- Positive thinking cannot replace a lack of safety.
- Emotional healing is impossible in a state of exhaustion.
- Purpose cannot emerge in the absence of human connection.
Mental health struggles are often needs deficits, not personal failures.
Clinical Insight
As a counselor, you may notice:
-
Anxiety clients often struggle with safety needs
-
Depressed clients often lack belonging or esteem
-
Burnout clients are blocked from self-actualization
-
Trauma survivors are stuck in survival mode
Effective healing requires meeting unmet needs—not just managing symptoms.
Final Reflection
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs is not outdated—it is misunderstood.
Modern life pushes people to chase the top of the pyramid while ignoring the foundation. True psychological well-being comes from alignment, safety, connection, self-worth, and meaning—in that order, and often repeatedly.
Healing is not about climbing the pyramid once.
It is about learning where you are—and giving yourself what you need.Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs in simple terms?
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs explains human motivation as a progression of needs—from basic survival (food, sleep, safety) to higher psychological growth (self-esteem, purpose, self-actualization). People are motivated to meet unmet needs, starting from the most basic.
2. Is Maslow’s Hierarchy still relevant in modern life?
Yes. While lifestyles have changed, human needs have not. In modern life, unmet needs often appear as stress, anxiety, burnout, relationship issues, and emotional emptiness, making Maslow’s framework highly relevant for mental health and counseling.
3. Can higher needs be pursued without meeting basic needs?
Partially—but not sustainably. For example, someone may pursue success or relationships while lacking sleep or emotional safety, but this often leads to burnout, anxiety, or dissatisfaction. Long-term well-being requires a stable foundation.
4. How does Maslow’s theory relate to mental health problems?
Many mental health symptoms are not disorders but signals of unmet needs:
Anxiety → unmet safety needs
Depression → unmet belonging or esteem needs
Burnout → blocked self-actualization
Therapy becomes more effective when these needs are addressed holistically.
5. What is self-actualization in real life?
Self-actualization means living in alignment with your values, abilities, and authentic self. It includes creativity, purpose, personal growth, and meaning—not perfection or constant happiness.
6. Why do people feel empty even after achieving success?
Because success without emotional safety, connection, and self-worth does not meet deeper psychological needs. This often reflects unmet belonging, esteem, or self-actualization needs.
7. How can therapy help with unmet needs?
Therapy helps identify where a person is stuck in the hierarchy, regulate the nervous system, heal past trauma, improve relationships, rebuild self-worth, and support purposeful living.
Written by Baishakhi Das
Counselor | Mental Health Practitioner
B.Sc, M.Sc, PG Diploma in Counseling
Reference
Abraham Maslow – Original theory
https://www.simplypsychology.org/maslow.html
American Psychological Association – Motivation & Humanistic Psychology
https://www.apa.orgNational Institute of Mental Health (NIMH) – Mental health foundations
https://www.nimh.nih.govWorld Health Organization – Mental health and well-being
https://www.who.int/teams/mental-health-and-substance-useMcLeod, S. (2023). Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs. Simply Psychology
https://www.simplypsychology.org/maslow.html- Information Processing Theory of Memory


3 Replies to “Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs in Modern Life:”