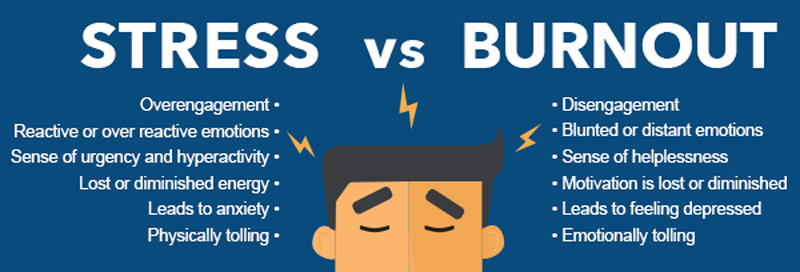
People come to you when everything goes wrong.
You remain composed when things are out of control and even when your own chest is tight.
You are a good listener, able to listen without interruption, a good non-judgemental holder of space, a problem-solver who is quiet enough to have your own feelings on the backburner.
And nobody seems to see when you are tired–because you have perfected concealing it.
It is commonly endorsed as resilience, maturity, or emotional intelligence to be the strong one. Your composure and steadiness is the admiration of people. However, under the admiration, there is an emotional price that is seldom realized. When strength becomes a role rather than a choice, it gradually becomes a burden, a burden that you bear without any more than an expression, without any protest, because that is what you are supposed to bear.
Your own strength, previously your safeguard, and formerly your strength, starts to suck you out. And not because you are weak, but because the greatest nervous system, the strongest system, must rest and have care and be supported.
The Invisible Contract of Strength
Most individuals grow up to be the strong one at a young age not necessarily of their choice, but due to circumstances. Grit was not an option; rather it was a coping mechanism of survival.
- You learned that you must not cry as it was the reliance of others that demanded you not to cry and express yourself, as it was unsafe or inconvenient.
- learned to contain emotions, instead of displaying them and turn feelings into something that could be controlled, and not shared.
- You were taught that you could postpone meeting your needs–sometimes forever–because keeping it together was the first before you put in your clothes.
This gradually leads to the establishment of an unwritten agreement with the world: I will remain calm in order to make other people feel safe.
You are the one that sticks, the one that can be depended on, the one that does not disintegrate at least not before anyone can notice.
With time, strength ceases to be a characteristic one draws and a character one lives within. And identities and those which are founded on survival are difficult to get out of, even when they have begun to cost you, your rest, your tenderness, and your feeling of being taken care of.
Emotional Labor Without Rest
Being the strong one can be doing all the time emotional work, the work that goes unseen, unpaid, and unrecognized.
- You also control your emotions so that you do not disturb other people and learn to make your pain as insignificant as possible to make their life comfortable.
- Take on the burden of other people without offloading your own, to be the vessel that holds the unhappy feelings that no one can express.
- You are the safe haven of the rest of them but you seldom get heard.
Slowly your nervous system is kept in a kind of silent watchfulness–in a permanent state of alertness, in an intermittent state of rest. You are held in position even when you are not in motion, trying to figure out what is going to happen next.
This is not draining you emotionally because you are weak, but this is not the purpose of human beings to shoulder emotional burden alone. Connection is to be two-way. The exhaustion is not a vice when the support is flowing in one way only: it is a biological and emotional phenomenon.
When Support Becomes One-Directional
Powerful individuals are commonly believed to be fine. Their silence is interpreted as the fact that nothing is amiss, and their quietness is perceived as power instead of the struggle.
-
No one, then, looks deep in–enquiries are superficial–asked at all.
- we are silent, therefore, thinking that it is stable and that we are not talking about pain, that it is not there.
-
Your limits are hardly ever questioned, as it is believed that you can do more, be more, take more.
Gradually, the requesting of assistance can gradually cease to occur, not because the need has been fulfilled, but because it no longer feels necessary to strain others, or because there are times when assistance has come at all when it has been requested. Needs are privatised, expectations are reduced and self-sufficiency is the surest way out.
Isolating emotionally is created gradually, not with a bang, but with a whimper, in the name of being independent. At first sight, it can seem to be strength. On the one hand, it can be rather like being alone with too much to be carried.
The Hidden Grief of the Strong
It is sorrowful to be the strong one–sorrow that is not much spoken, and is seldom named, and has to be borne by the individual.
- Sorrow in the embrace that you did not have at the time you needed it the most.
- The sweetness which you had delayed, and said you would sleep by and by, and feel by and by, and be by and by.
- Sorrow over the weakness you ingested, knowing since you were young that weakness can be neither safe nor desirable to express.
Accomplishing this sadness, there might also be guilt in desiring rest as though fatigue is a personal vice. Shame can be experienced in being tired when you are managing everything. And confusion may come to rest in where nothingness appears despite doing everything and keeping it all together.
But emotional exhaustion is not failure–it is a message. A silent communication of your nervous system requesting you to be noticed, nurtured and given to take a break after carrying too much far too long.
Strength Is Not the Absence of Need
Emotional suppression is not a strength.
It is not being quiet, accepting whatever, or doing it by any means.
Emotional honesty is the real strength and that is the strength to be truthful to what is in your heart.
It is permitting oneself to say, without any explanation or apology:
- “I’m not okay today.”
- “need support too.”
- “I don’t have to earn rest.”
The process of healing starts with strength being loose instead of hard, with stamina being soft as well as strong, with self-reliance allowing connection. You do not need to work hard to earn your safety, when you permit yourself to be grasped, not to grasp others, your nervous system comes to understand that you do not need to work hard to get safety. There are cases when it is just received.
Relearning Balance
When you are the strong, ask yourself–ask him–ask me–ask him:
And when I am not okay, where did I get to know that I always have to be okay?
What will I be when I cease to act out resilience and permit myself to exist?
What do you think it would be like to have that same care, patience and understanding given to me with the same free hand that I so readily dispense to others?
Such questions are not to be answered in a short period. They are entreaties to observe that which has long been carried.
- Resting does not make you lose your power.
- Do not shrink into ineptitude by seeking assistance.
- It is not being a human that disappoints anyone.
Power was not supposed to entail self-abandonment. It was to be combined with tenderness, support and rest.
A Reframe Worth Remembering
You are not so tough in that you can take everything and not break.
You are tough since you evolved-because you studied to live in places where you needed to be strong before you were prepared to be strong.
- Now you may have something new.
- Connection over endurance.
- Support over silence.
- Power.
When you rest you do not lose your strength. It evolves. It is something that you live on, not something that you pay on.
FAQs
1. Why is it so emotionally exhausting to be the strong one?
Since it is a matter of constant emotional control, personal needs repression, and one-sided aid, exhausting the nervous system in the long run.
2. Does emotional exhaustion mean one is weak?
No. Emotional exhaustion is a biological and mental reaction to the stress and to unmet emotion needs over a long period of time.
3. Why do powerful individuals hardly obtain support?
They are presumed to be fine and that is why other people forget that they need to be cared about and have emotional check-ins.
4. Is there a role of childhood experiences that forms the strong one?
Yes. Strength is taken by many as an early survival tactic in an emotionally unsafe or demanding environment.
5. What is emotional labor?
Emotional labor is the process of controlling emotions – yours and those of other people – to ensure stability, comfort or harmony.
6. What is the impact of emotion suppression on mental health?
It exerts more stress, emotional numbness, anxiety, burnout, and may lead to depression in the long run.
7. Why has it happened that tough individuals are guilty of taking a break?
Since being useful, enduring, or responsible has already associated the self-worth of the person, rest might feel unworthy.
8. What is it like to experience nervous system exhaustion?
Constant fatigue, emotional detachment, irritability, hyper vigilance, inability to relax or being empty.
9. Is it always healthy to be independent?
Not when it covers emotional isolation. The capacity to be assisted is also a part of healthy independence.
10. How can powerful individuals embark on seeking assistance?
Their small steps can help them: first naming their feelings, selective sharing, and reminding themselves that support is not their responsibility.
11. What does it mean by trauma-informed strength?
Power which is flexible, emotional integrity, rest and relationship as opposed to perpetual effort.
12. Do we need therapy among people who are always strong?
Yes. In therapy there is a safe space where suppressed emotions are relieved and learning reciprocal care re-learned.
13. Why is it that being strong causes burnout?
The continuous self-control in the absence of emotional discharge is too much to the mind and body.
14. What is your ratio of strength and softness?
Trying to be vulnerable, demarcating boundaries and providing yourself with the kind of care you provide to others.
15. How do you begin healing the emotional fatigue?
Not being ashamed of feeling tired and allowing yourself to require assistance.
Written by Baishakhi Das
Counselor | Mental Health Practitioner
B.Sc, M.Sc, PG Diploma in Counseling
✅ Reference
-
American Psychological Association – Stress & Burnout
https://www.apa.org/topics/stress -
National Institute of Mental Health – Coping With Stress
https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/topics/stress -
Polyvagal Theory & Nervous System Regulation – Dr. Stephen Porges
https://www.polyvagalinstitute.org -
Emotional Labor & Mental Health – Psychology Today
https://www.psychologytoday.com/us/basics/emotional-labor -
Trauma and the Body – Bessel van der Kolk
https://www.traumaresearchfoundation.org - Feeling Behind “Not Good Enough”
This topic performs well due to rising searches around men’s mental health, workplace stress, and burnout recovery. Combining emotional insight with practical steps increases engagement and trust.