Introduction: The Crisis of Modern Love
We live in an age where people are more connected than ever—but relationships are breaking faster than before. Ghosting, sudden breakups, emotional distance, communication issues, and commitment fears are becoming the norm for many couples.
People often blame technology, dating apps, or “lack of loyalty,” but modern relationship breakdown is far more psychological than cultural. Beneath most conflicts, misunderstandings, and emotional wounds lies one core concept:
Our attachment style shapes how we love, fight, connect, and break apart.
Attachment theory, developed by John Bowlby and expanded by Mary Ainsworth, explains why some people seek closeness, others push away, and some feel torn between the two. When attachment needs are unmet or mismatched, relationships struggle—even when both partners love each other deeply.
This article explores:
-
Why modern relationships fail
-
How attachment styles develop
-
The role of anxious, avoidant, and disorganized attachment
-
The “anxious-avoidant trap”
-
Why secure attachment is rare today
-
How to build healthier relationships
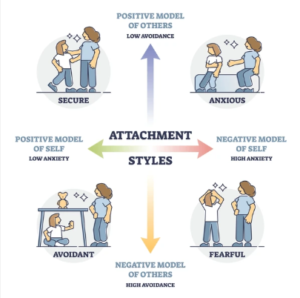
Section 1: What Is Attachment Theory?
Attachment theory explains how early bonding with caregivers forms “internal working models,” which shape adult romantic relationships.
Your attachment style determines:
-
How you express love
-
How you deal with conflict
-
How much closeness you need
-
How you handle rejection
-
How you communicate
-
How safe or unsafe relationships feel
The Four Main Attachment Styles
-
Secure
-
Anxious (Preoccupied)
-
Avoidant (Dismissive)
-
Disorganized (Fearful-Avoidant)
Most relationship dysfunction stems from insecure attachment: anxious, avoidant, or disorganized.

Section 2: Why Modern Relationships Fail—The Attachment Perspective
Today’s relationships face unique challenges:
1. Emotional Needs Are Higher Than Ever
People expect partners to be:
-
Best friend
-
Lover
-
Therapist
-
Motivator
-
Companion
-
Financial supporter
-
Safe space
These expectations create pressure and disappointment.
2. Childhood Trauma Is More Recognized but Less Healed
Many adults:
-
Grew up with emotionally unavailable parents
-
Had inconsistent caregivers
-
Experienced neglect or overprotection
-
Carry unresolved trauma
Unhealed wounds create insecure attachment patterns.
3. Technology Intensifies Anxiety
Read receipts, texting delays, social media comparison, and online dating can trigger attachment insecurity.
4. Independence Culture Clashes with Emotional Needs
Society rewards:
-
Self-reliance
-
Detachment
-
Hustle culture
But relationships require vulnerability and interdependence.
5. People Choose Partners Based on Familiar Trauma
We subconsciously pick partners who recreate childhood emotional patterns—even if they hurt us.
Section 3: The Role of Childhood in Adult Attachment
Secure Attachments Develop When Childhood Needs Are Met
Children learn:
“I am loved. My feelings matter. People are safe.”
These adults create stable, emotionally fulfilling relationships.
Insecure Attachments Form When Needs Are Inconsistently Met
-
Emotional neglect
-
Unpredictable parenting
-
Criticism
-
Lack of affection
-
Over-controlling parents
These lead to adult struggles in intimacy, boundaries, trust, and communication.
Section 4: Anxious Attachment – “Do You Really Love Me?”
What It Feels Like
Anxiously attached adults fear abandonment.
They crave closeness but are terrified they will be rejected or replaced.
Signs of Anxious Attachment
-
Overthinking texts or conversations
-
Need for constant reassurance
-
Fear of being alone
-
Jealousy or comparison
-
Difficulty trusting
-
Emotional hyperactivation during conflict
-
Feeling “too much” or “too needy”
How They Behave in Relationships
They often:
-
Cling
-
Chase
-
Overcommunicate
-
Apologize excessively
-
Accept unhealthy behavior to avoid breakups
Why Modern Relationships Fail With Anxious Attachment
Because emotional needs feel urgent and intense, anxious partners can overwhelm or scare avoidant partners away.

Section 5: Avoidant Attachment – “I Need Space”
What It Feels Like
Avoidantly attached adults fear intimacy.
Closeness threatens their independence and sense of control.
Signs of Avoidant Attachment
-
Difficulty identifying emotions
-
Keeping partners at a distance
-
Fear of “being trapped”
-
Discomfort with vulnerability
-
Shutting down during conflict
-
Preferring logic over emotional expression
How They Behave in Relationships
They often:
-
Withdraw
-
Delay commitment
-
Ghost or go silent
-
Minimize problems
-
Value independence over closeness
Why Modern Relationships Fail With Avoidant Attachment
Avoidant partners disconnect during emotional moments—leading the anxious partner to pursue harder, creating a toxic cycle.
Section 6: Disorganized Attachment – “Come Close, But Don’t Hurt Me”
Also called fearful-avoidant, this style is the most conflicted and confusing.
What It Feels Like
These individuals crave love but fear intimacy, usually due to trauma or chaotic childhoods.
Signs of Disorganized Attachment
-
Mood swings
-
Instability in relationships
-
Fear of rejection AND fear of closeness
-
Sabotaging healthy relationships
-
Attracting toxic partners
-
Slow healing after breakups
Why Modern Relationships Fail With Disorganized Attachment
These individuals may attach intensely and then suddenly pull away. Both partners feel confused and unsafe.
Section 7: Secure Attachment – “Love Is Safe”
Signs of Secure Attachment
-
Comfortable with closeness
-
Communicate clearly
-
Healthy boundaries
-
No fear of losing partner
-
Steady emotional presence
Why Secure Attachment Is Rare Today
-
More childhood emotional neglect
-
More pressure on individuals
-
More fractured families
-
Growing anxiety culture
-
Digital overstimulation
Modern society produces insecure attachment at a high rate.
Section 8: The Anxious-Avoidant Trap (Most Common Reason for Breakups)
This dynamic explains MOST modern relationship breakdowns.
The Cycle
-
The anxious partner wants closeness.
-
The avoidant partner withdraws.
-
The anxious partner panics and pursues harder.
-
The avoidant partner distances more.
-
Both feel misunderstood.
-
Breakup happens.
-
They often repeat the same cycle with new partners.
Why This Happens
Each partner activates the other’s deepest wounds:
-
Anxious: “Don’t leave me.”
-
Avoidant: “Don’t control me.”
Modern dating apps actually pair these types frequently, because avoidants are charming at first and anxious partners are expressive.
Section 9: Why Technology Makes Attachment Worse
1. Instant messaging increases anxiety
Waiting for replies triggers fear of abandonment.
2. Social media increases comparison
Perfect couples online worsen insecurity.
3. Dating apps create illusion of endless options
Avoidants avoid commitment; anxious people feel rejected.
4. Overstimulation affects emotional regulation
Constant dopamine crashes reduce patience and empathy.
Section 10: Emotional Unavailability – A Modern Epidemic
People today are:
-
Burnt out
-
Overworked
-
Distracted
-
Overstimulated
This creates emotional numbness and detachment, ruining relationship quality.
Signs your partner is emotionally unavailable
-
Avoiding serious discussions
-
Shutting down during conflict
-
Keeping you at a distance
-
Inconsistent affection
-
Fear of labels or commitment
Attachment wounds trigger unavailability.
Section 11: Why Communication Fails in Modern Relationships
Communication breaks because attachment needs conflict.
Anxious communicator
-
Over-communicates
-
Needs reassurance
-
Wants emotional connection
Avoidant communicator
-
Under-communicates
-
Avoids emotions
-
Prefers logic over feelings
Result:
Misunderstandings, frustration, emotional distance, repeated arguments.
Section 12: Why People Choose the Wrong Partners
1. Familiar trauma feels like love
If chaos was normalized early, safety feels boring.
2. Chemistry often signals unresolved wounds
People confuse intensity with intimacy.
3. Fear of vulnerability attracts avoidants
People choose partners who confirm their fears.
4. People choose based on unmet childhood needs
Not compatibility.

Section 13: The Psychology Behind Modern Breakups
Breakups today are faster because:
-
Emotional tolerance is low
-
Expectations are high
-
Communication is digital, not emotional
-
People fear vulnerability
-
Past trauma remains unresolved
-
Secure attachment is rare
Attachment needs often go unmet because individuals lack tools to understand themselves and each other.
Section 14: How to Build Healthy, Secure Relationships
1. Heal Your Attachment Style
Self-awareness is the first step. Understand your patterns.
2. Learn Emotional Regulation Skills
Breathing, grounding, DBT techniques, mindfulness.
3. Communicate Needs Clearly
Secure partners express needs without fear or pressure.
4. Avoid Triggering Dynamics
Anxious & avoidant pairings require conscious work.
5. Practice Vulnerability
Healthy relationships require emotional openness.
6. Set Boundaries With Love
Not walls—boundaries create safety.
7. Choose Partners Based on Emotional Safety
Not intensity, chemistry, or trauma familiarity.
Conclusion: Love Fails When Attachment Needs Go Unseen
Modern relationships don’t fail because people don’t care.
They fail because:
-
People are unhealed.
-
People fear vulnerability.
-
People misunderstand themselves.
-
People choose partners who trigger their wounds.
Attachment theory reveals one truth:
Relationships succeed not because people are perfect, but because they feel emotionally safe.
Understanding attachment styles can transform not just your love life—but your entire emotional world.
Reference
American Psychological Association (APA)
National Institute of Mental Health — Attachment & Trauma
The Gottman Institute (Leading Relationship Research)
Relationship Red Flags Backed by Psychology
Anxious vs Avoidant Partners: The Push–Pull Pattern




One Reply to “Why Modern Relationships Fail: Attachment Theory Explained”